Infections and type 2 diabetes
Every health theory needs a colorful pyramid, so here is one to show the progression from chronic infections to type 2 diabetes.
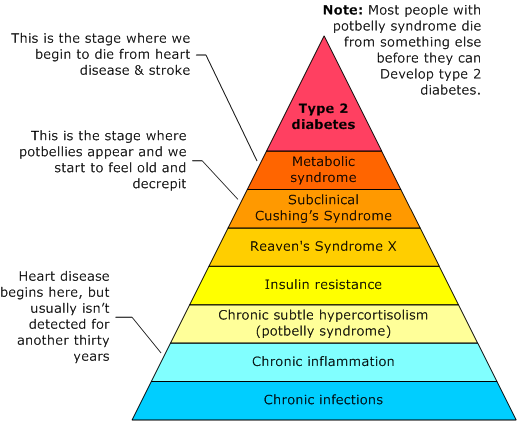
Each stage lasts until the stage before it is cured, or the patient dies. Consequently, the later stages overlap the earlier stages--that's why people with type 2 diabetes have so many inflammatory disorders.
More information on type 2 diabetes
Chapters 7, 8, and 13 of The Potbelly Syndrome give more information on how infections lead to insulin resistance and diabetes.
Fernández-Real JM, Pickup JC. Innate immunity, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Jan;19(1):10-6. Epub 2007 Dec 21.
Koehler C, Ott P, Benke I, Hanefeld M. Comparison of the Prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome by WHO, AHA⁄NHLBI, and IDF Definitions in a German Population with Type 2 Diabetes: The Diabetes in (DIG) Study. Horm Metab Res. 2007 Sep;39(9):632-5.
Zhao P, Wang JB, Jiao J. [Investigation on the incidence of diabetes in chronic hepatitis C patients and their HCV genotypes] Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2006 Feb;14(2):86-8. Chinese.
Fernández-Real JM. Genetic predispositions to low-grade inflammation and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2006 Feb;8(1):55-66. Review.
Vondra K, Hampl R. [Glucocorticoids and diabetes mellitus] Vnitr Lek. 2006 May;52(5):493-7. Review. Czech.
Chiodini I, Torlontano M, Scillitani A, Arosio M, Bacci S, Di Lembo S, Epaminonda P, Augello G, Enrini R, Ambrosi B, Adda G, Trischitta V. Association of subclinical hypercortisolism with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a case-control study in hospitalized patients. Eur J Endocrinol. 2005 Dec;153(6):837-44.
Tenenbaum A, Fisman EZ, Motro M. Metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus: focus on peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (PPAR). Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2003 Mar 23;2:4.
Tauchmanova L, Rossi R, Biondi B, Pulcrano M, Nuzzo V, Palmieri EA, Fazio S, Lombardi G. Patients with subclinical Cushing's syndrome due to adrenal adenoma have increased cardiovascular risk. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Nov;87(11):4872-8.
Mendis S, Arseculeratne YM, Withana N, Samitha S. Chlamydia pneumoniae infection and its association with coronary heart disease and cardiovascular risk factors in a sample South Asian population. Int J Cardiol. 2001 Jul;79(2-3):191-6.
Kern W, Stange EF, Fehm HL, Klein HH. [Glucocorticoid-induced diabetes mellitus in gastrointestinal diseases] Z Gastroenterol. 1999 Jun;Suppl 1:36-42. Review. German.
